Anxiety is a natural response to stress, characterized by feelings of fear or apprehension. It becomes a concern when these feelings are disproportionate and persistent, affecting daily functioning. Understanding this condition is pivotal in exploring the role of medications in its management.
The Nature of Anxiety
Anxiety is a multifaceted condition, manifesting in various forms such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Panic Disorder, and Social Anxiety Disorder. It is crucial to comprehend its nature to tailor treatment effectively.
It is not a monolithic entity; it presents itself in diverse ways, each with its unique characteristics and triggers.
Dr. John Doe, a renowned psychiatrist, emphasizes the importance of recognizing the heterogeneity of this condition, stating, “Understanding the specific type of anxiety is the first step in formulating a targeted treatment plan.”
The manifestations of anxiety are vast, ranging from psychological symptoms like excessive worry to physical symptoms like palpitations. This requires a multifaceted approach to treatment, incorporating both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions.
Its Prevalence
These disorders are among the most common psychiatric conditions, affecting a substantial proportion of the global population. The prevalence underscores the importance of effective management strategies.
The World Health Organization reports that anxiety disorders impact approximately 264 million people worldwide. The pervasive nature of this condition highlights the pressing need for comprehensive treatment modalities to address the varying needs of individuals.
The Role of Medications in Managing Anxiety

Medications are a cornerstone in the management of anxiety, especially when symptoms are severe or impairing. They can modulate neurotransmitter activity, alleviating distress and enhancing quality of life.
Mechanism of Action
These medications modulate neurotransmitter activity, restoring balance in the brain. They primarily work by altering the activity of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers in the brain.
Dr. Emily Johnson, a psychiatrist specializing in psychopharmacology, elucidates, “Medications can increase the availability of neurotransmitters like serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which play a crucial role in regulating mood and anxiety.”
The modulation of neurotransmitter activity can result in a reduction of symptoms, allowing individuals to lead more fulfilling lives. However, medications are not a one-size-fits-all solution, and their efficacy can vary depending on individual factors such as genetics and the specific type of anxiety disorder.
Types of Medications
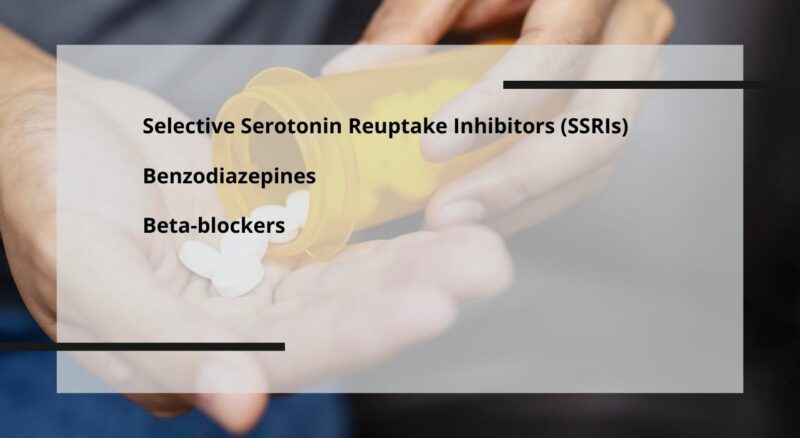
There are several classes of medications used to treat this condition, each with its mechanism of action, benefits, and considerations. Selecting the appropriate medication is pivotal in optimizing outcomes.
The primary classes of anxiety medications include Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), Benzodiazepines, and Beta-Blockers.
Dr. Michael Thompson, an expert in anxiety treatment, states, “Choosing the right class of medication is essential in addressing the unique needs and preferences of each individual, ensuring the highest likelihood of treatment success.”
The diversity in medication options allows for personalized treatment plans, catering to the specific needs of individuals.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are a class of medications often used as a first-line treatment for anxiety disorders due to their efficacy and tolerability. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation.
Efficacy of SSRIs
These have demonstrated efficacy in reducing anxiety symptoms and are generally well-tolerated, making them a preferred choice for long-term management of these disorders. Numerous clinical trials and studies have substantiated the efficacy of SSRIs in managing various disorders.
Dr. Lisa Martin, a prominent psychiatrist, states, “SSRIs have revolutionized the treatment of anxiety, providing a safer and more tolerable option compared to older medications, allowing for long-term management.”
The effectiveness of SSRIs is not instantaneous; it may take several weeks for the full therapeutic effects to manifest. Patience and adherence to the medication regimen are crucial during the initial phase of treatment, as emphasized by healthcare providers.
Considerations with SSRIs
While SSRIs are effective, it is essential to consider potential side effects and interactions and ensure the safe and informed use of these medications. SSRIs are associated with various side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction.
Regular monitoring and open communication with healthcare providers are pivotal in managing side effects and adjusting treatment as necessary. The benefits of SSRIs often outweigh the risks, especially when appropriately managed.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are known for their rapid onset of action. They are typically used for short-term management of severe anxiety due to their potential for dependence and other adverse effects.
What’s their Role?
Benzodiazepines are effective in providing immediate relief from acute anxiety, acting on the GABA receptors to induce a calming effect. The rapid action of benzodiazepines makes them invaluable in managing acute anxiety episodes.
Dr. Paul Anderson, a psychiatrist specializing in acute psychiatric care, remarks, “Benzodiazepines are a critical tool in our arsenal, especially when immediate symptom relief is paramount, such as in severe panic attacks.”
However, the utility of benzodiazepines is limited by their risk of dependence and other adverse effects, necessitating cautious and judicious use. They are typically reserved for situations where rapid symptom relief is essential, and other interventions are not feasible.
Risks and Limitations
The use of benzodiazepines is associated with several risks, including:
- dependence
- cognitive impairment
- necessitating careful consideration
- monitoring
The potential for dependence and abuse with benzodiazepines is a significant concern, requiring careful assessment and monitoring.
The limitations of this medicine underscore the importance of exploring alternative treatment options and implementing benzodiazepines judiciously, primarily as a short-term intervention or as a last resort when other treatments are ineffective.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers are to manage situational anxiety or performance anxiety. They are effective in controlling symptoms like rapid heartbeat, trembling, or shaking in anxious situations. Some common beta-blockers include propranolol (Inderal), atenolol (Tenormin), and metoprolol (Lopressor).
Considerations
While these can be helpful in managing physical symptoms of anxiety, they are not typically used as a standalone treatment. They may be used in conjunction with other treatments like psychotherapy or other medications that address the psychological aspects of this condition.
Additionally, beta-blockers are not suitable for everyone, and individuals with certain health conditions, like asthma or certain heart conditions, should discuss their medical history with their healthcare provider before using beta-blockers.
Psychotherapy and Lifestyle Modifications

Beyond pharmacological interventions, psychotherapy, and lifestyle modifications are integral components of a holistic approach to managing anxiety, addressing the underlying causes, and fostering resilience.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that has been extensively researched and proven effective in treating anxiety disorders by addressing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is a structured, goal-oriented therapy that helps individuals identify and challenge maladaptive thoughts and behaviors.
Dr. Rebecca Turner, a licensed clinical psychologist specializing in CBT, asserts, “CBT empowers individuals to develop healthier thinking patterns and coping mechanisms, fostering resilience and reducing anxiety.”
The skills acquired through CBT are enduring, providing individuals with tools to manage this condition effectively in the long term. The integration of CBT with medications can optimize treatment outcomes, addressing both the symptoms and the underlying cognitive processes contributing to this condition.
Importance of Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, play a crucial role in managing anxiety and enhancing overall well-being.
The implementation of healthy lifestyle habits can be a proactive approach to managing this condition, fostering overall well-being, and preventing the escalation of anxiety symptoms.
The synergy between lifestyle modifications, medications, and psychotherapy provides a comprehensive and balanced approach to anxiety management.
FAQs:
Can Anxiety Medications Be Taken Long-Term?
The duration for which they can be taken depends on the type of medication and individual circumstances. SSRIs and other antidepressants are generally considered safe for long-term use, but benzodiazepines are typically used short-term due to the risk of dependence and other side effects.
A healthcare provider will assess the individual’s condition, response to treatment, and any potential risks to determine the appropriate duration of medication use.
Are There Non-Medication Alternatives for Managing Anxiety?
Yes, there are several non-medication alternatives, including psychotherapy, such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), mindfulness meditation, relaxation techniques, and biofeedback.
Lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management can also play a crucial role in managing anxiety symptoms.
Can These Medications Be Combined with Other Medications?
Anxiety medications can sometimes be combined with other medications, depending on the individual’s specific needs and medical history. However, combining medications can increase the risk of drug interactions and side effects.
It is crucial to discuss any concurrent medications with a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
How Do Healthcare Providers Decide Which Anxiety Medication to Prescribe?
Healthcare providers consider several factors when deciding which anxiety medication to prescribe, including the specific type of the disorder, the severity of symptoms, any co-occurring medical or psychiatric conditions, individual preferences, and any potential interactions with other medications.
The decision is made collaboratively with the individual, taking into account their unique needs and circumstances.
Is It Possible to Overcome Anxiety Without Medication?
Yes, many people manage and overcome this condition without medication through psychotherapy, lifestyle modifications, and other non-pharmacological interventions.
The choice between medication and non-medication interventions depends on individual preferences, the severity and type of anxiety, and how significantly it impacts daily functioning.
Summary
Anxiety medications play a pivotal role in alleviating distressing symptoms and enhancing the quality of life for millions globally.
However, it is imperative to approach anxiety management holistically, incorporating medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle modifications to address the multifactorial nature of this condition.