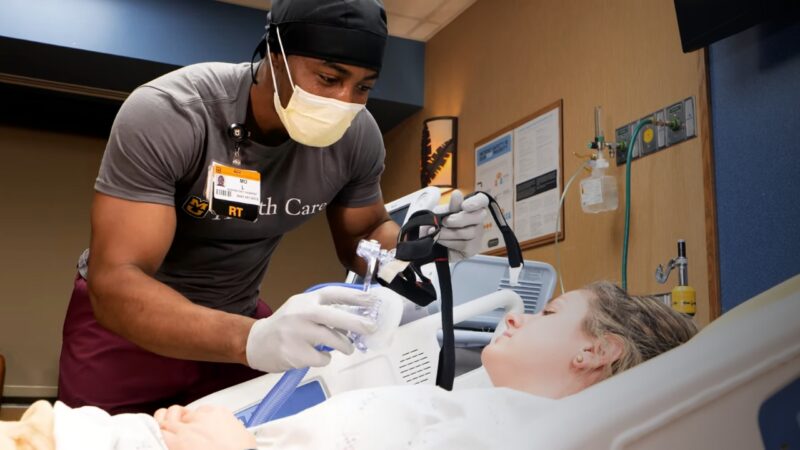
In the complex landscape of healthcare, Long-Term Acute Care (LTAC) facilities play a critical role. These specialized hospitals are designed to provide extended medical and rehabilitative care for patients with serious health conditions that require a longer hospital stay. LTAC facilities are often a bridge between the intensive care unit (ICU) and a lower level of care, such as a skilled nursing facility or home care. They provide a setting where patients can receive comprehensive, multidisciplinary care while they recover from their acute illness or injury.
The purpose of LTAC facilities is to cater to patients who are too ill to be discharged home or to a lower level of care but no longer require the intensive services of a traditional acute care hospital. These patients often have complex medical needs, such as ventilator weaning, wound care, and rehabilitation, that require specialized care and a longer recovery period. Facilities are equipped to provide this level of care, with a focus on improving patients’ functional status and quality of life.
While Facilities are part of the broader healthcare system, they are distinct from other healthcare settings in several ways. Unlike traditional hospitals, which are designed for short-term, intensive care, LTAC facilities provide care over a longer period, typically 25 days or more. They also differ from skilled nursing facilities and rehabilitation centers, which provide lower-intensity care and are more focused on rehabilitation and recovery. Facilities are uniquely positioned to provide a level of care that is both intensive and long-term, meeting the needs of a specific patient population.
The Role of LTAC Facilities in Patient Care
LTAC facilities provide specialized care for medically complex patients. These patients often have multiple chronic conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory disease, that require ongoing management. They may also have acute conditions, such as infections or wounds, that need intensive treatment. Facilities are equipped to manage these complex cases, with a team of healthcare professionals who have specialized training and expertise in long-term acute care.
The relationship between facilities and referring hospitals is a collaborative one. When a patient is ready to be discharged from the ICU but still needs a high level of care, the hospital and the LTAC facility work together to ensure a smooth transition. The facility receives detailed information about the patient’s condition and treatment plan, and the hospital team remains involved in the patient’s care, providing consultation and support as needed.
Eligibility for LTAC admission is determined based on a patient’s medical condition and level of care needs. Patients who are eligible for LTAC care typically have severe or complex medical conditions that require intensive treatment and a longer recovery period. They may also have functional or cognitive impairments that require rehabilitation and support. The decision to admit a patient to an LTAC facility is made by a team of healthcare professionals, including the patient’s primary care physician, specialists, and case manager.
The Multidisciplinary Team in LTAC Facilities
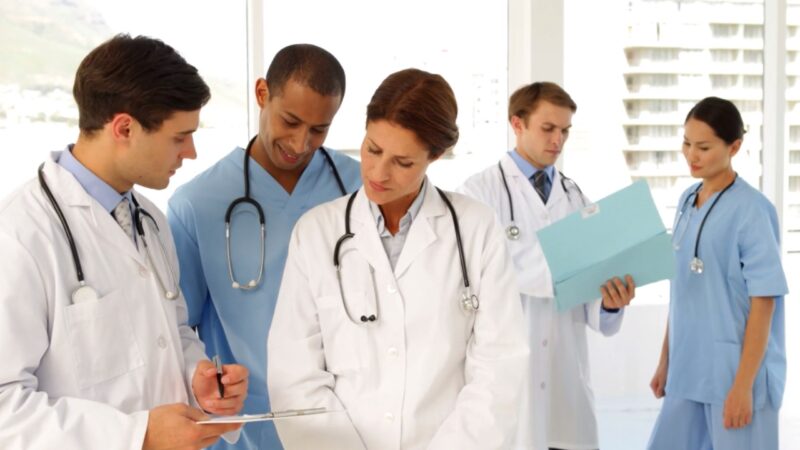

The care team in an LTAC facility is a multidisciplinary one, comprising a variety of healthcare professionals. This team typically includes physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, physical and occupational therapists, dietitians, social workers, and case managers. Each member of the team plays a unique role in the patient’s care, contributing their expertise to the development and implementation of the patient’s treatment plan.
Collaboration and coordination among different specialties are key to the success of care. The multidisciplinary team meets regularly to discuss each patient’s progress, review the treatment plan, and make any necessary adjustments. This collaborative approach ensures that all aspects of the patient’s care are integrated and that the patient’s needs are being met in a comprehensive and coordinated way.
The role of the multidisciplinary team extends beyond the provision of medical care. The team also addresses the patient’s psychological, social, and functional needs, helping them to cope with the challenges of their illness and to work towards their recovery goals. This holistic approach to care is a hallmark of facilities, reflecting their commitment to treating the whole person, not just the illness.
Services and Treatments Offered in LTAC Settings
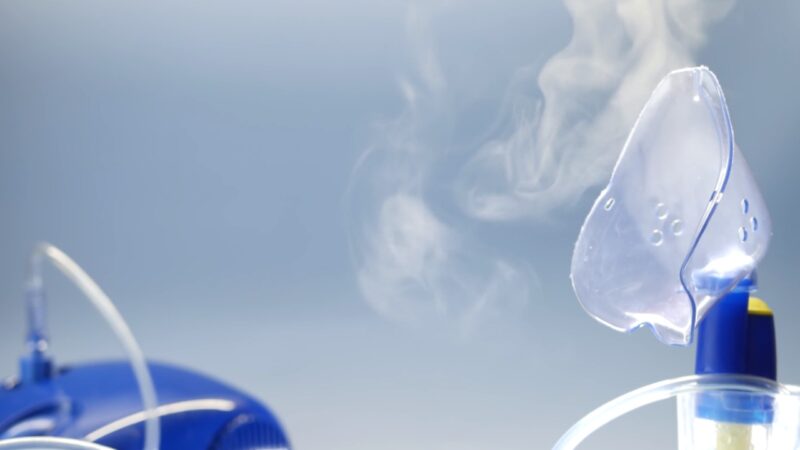

One of the key services provided in settings is ventilator management and respiratory therapy. Many patients in LTAC facilities require ventilator support due to respiratory failure or other serious conditions. The respiratory therapy team in a facility is skilled in managing complex ventilator cases, including weaning patients off the ventilator when they are ready.
Wound care, infection control, and antibiotic therapy are also important aspects of LTAC care. Patients with complex wounds, such as pressure ulcers or surgical wounds, receive specialized wound care to promote healing and prevent complications. Infection control measures are in place to prevent the spread of infections, and antibiotic therapy is provided as needed to treat existing infections.
In addition to these specialized services, LTAC facilities also provide a range of other treatments and therapies, including intravenous (IV) therapy, dialysis, pain management, and palliative care. These services are tailored to the individual patient’s needs and are provided as part of a comprehensive, coordinated care plan.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
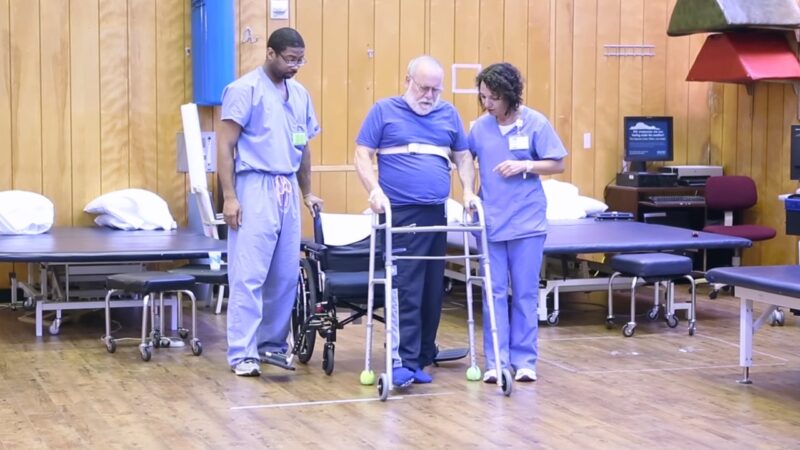

Rehabilitation is a crucial part of the care provided in facilities. Many patients in care have experienced a loss of function due to their illness or injury and require rehabilitation to regain their abilities. The rehabilitation team in a facility includes physical and occupational therapists who work with patients to improve their strength, mobility, and independence.
Each patient’s rehabilitation program is personalized to their needs and goals. The therapists conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s functional abilities and work with the patient and their family to develop a treatment plan. This plan includes a range of therapies and exercises designed to improve the patient’s physical function and help them return to their daily activities.
In addition to physical therapy, many patients in LTAC care also receive occupational therapy. Occupational therapists help patients to regain the skills needed for daily living, such as dressing, bathing, and cooking. This therapy is an important part of the patient’s recovery, helping them to regain their independence and improve their quality of life.
Nutritional Support in Facilities

Nutritional support is another key aspect of LTAC care. Many patients in these facilities have unique dietary needs due to their medical conditions. For example, patients with diabetes may need a diet that helps to control their blood sugar levels, while patients with kidney disease may need a diet that is low in certain nutrients.
Dietitians play a crucial role in LTAC facilities, working with patients and their families to develop a personalized nutrition plans. This plan takes into account the patient’s medical condition, dietary preferences, and nutritional needs. The dietitian also provides education and counseling to help patients understand their diet and make healthy food choices.
In addition to providing individualized nutrition plans, LTAC facilities also offer nutritional support services, such as tube feeding for patients who are unable to eat by mouth. These services are provided by a team of healthcare professionals, including dietitians, nurses, and physicians, who work together to ensure that patients receive the nutrition they need to recover and thrive.
Emotional and Psychological Support

Managing patients’ emotional well-being is a critical part of LTAC care. Many patients in LTAC facilities are dealing with the stress and anxiety of a serious illness, and they may also be coping with the emotional impact of a prolonged hospital stay. Facilities provide a range of support services to help patients manage these challenges, including counseling, support groups, and mental health resources.
Counseling services in LTAC facilities are provided by a team of professionals, including psychologists, social workers, and chaplains. These professionals provide individual and group counseling, helping patients to cope with their feelings, manage stress, and maintain a positive outlook. They also provide support to families, helping them to understand and cope with the challenges of their loved one’s illness.
In addition to counseling, LTAC facilities also provide resources to support patients’ mental health. This may include access to psychiatric services, medication management, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. These services are tailored to the individual patient’s needs and are provided as part of a comprehensive, coordinated care plan.
Transitioning from LTAC to Home or Lower Level of Care

The goal of LTAC care is to help patients recover to the point where they can transition to a lower level of care or return home. This transition is a critical phase of the patient’s recovery and requires careful planning and coordination. The discharge planning process begins as soon as the patient is admitted to the LTAC facility, with the goal of ensuring a smooth and successful transition.
The discharge planning team in a facility includes a case manager, who coordinates the patient’s care and communicates with the patient, their family, and the healthcare team. The case manager works with the patient and their family to develop a discharge plan, which includes arrangements for follow-up care, home health services, and any necessary equipment or supplies.
Ensuring a smooth transition for patients and their families is a priority for LTAC facilities. This includes providing education and support to help patients manage their health at home, coordinating with other healthcare providers to ensure continuity of care, and following up with patients after discharge to address any issues or concerns.
Quality and Safety Standards
LTAC facilities are subject to stringent quality and safety standards. These standards are set by regulatory bodies, such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), and accreditation organizations, such as The Joint Commission. facilities must meet these standards to receive accreditation and participate in Medicare and Medicaid programs.
The quality and safety standards for LTAC facilities cover a wide range of areas, including patient care, infection control, medication management, and patient rights. These standards are designed to ensure that patients receive safe, high-quality care and that their rights are protected.
In addition to meeting regulatory and accreditation standards, facilities also engage in continuous quality improvement efforts. This includes monitoring performance metrics, conducting patient satisfaction surveys, and implementing quality improvement projects. These efforts are aimed at improving patient outcomes, enhancing patient satisfaction, and ensuring the highest level of care.
Challenges and Future Directions in LTAC Care

Like all sectors of healthcare, LTAC faces its own set of challenges. Financial considerations, including reimbursement models and the cost of providing high-quality care, are a major concern. LTAC facilities must navigate complex reimbursement systems, which often do not fully cover the cost of the intensive, long-term care that LTAC patients require.
Innovations in technology and patient monitoring are shaping the future of LTAC care. Advanced technologies, such as telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, are being integrated into care, enhancing the ability to monitor patient’s health and deliver care. These technologies have the potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and increase access to LTAC care.
Despite these challenges, the future of LTAC care is promising. With growing recognition of the value of LTAC in the continuum of care and ongoing advancements in medical technology, LTAC facilities are well-positioned to continue providing high-quality, specialized care for medically complex patients.
Patient Stories: Successes and Challenges in LTAC
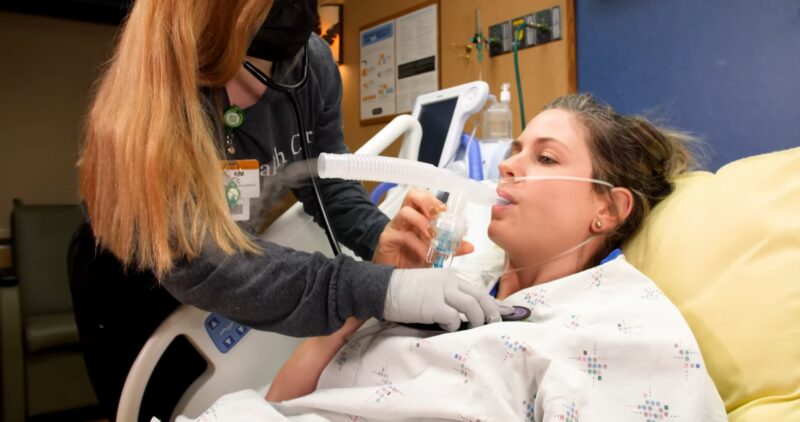
Patient stories provide a powerful testament to the successes and challenges of LTAC care. These real-life accounts offer a glimpse into the experiences of patients and their families, highlighting the resilience, determination, and courage that characterize the journey through LTAC care.
One such story is that of a patient who, after a severe stroke, was admitted to an LTAC facility. Despite the challenges of her condition, she made remarkable progress, thanks to the intensive rehabilitation and personalized care she received. Her story is a testament to the power of LTAC care to transform lives and foster recovery.
But LTAC care is not without its challenges. Another patient, battling a complex wound and multiple chronic conditions, faced numerous setbacks during his LTAC stay. Yet, through the dedicated care of the LTAC team and the support of his family, he was able to overcome these challenges and make significant strides in his recovery.
These stories underscore the vital role of LTAC facilities in caring for medically complex patients. They also highlight the need for ongoing support and resources to ensure that all patients have access to the high-quality, specialized care that facilities provide.
Conclusion

In conclusion, LTAC facilities play a vital role in the healthcare system. They provide specialized, long-term care for medically complex patients, bridging the gap between intensive care and lower levels of care. With a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals and a comprehensive range of services, facilities are uniquely equipped to meet the needs of this patient population.
The value of LTAC care is evident in the stories of patients who, despite serious illness and complex medical needs, have made remarkable progress in their recovery. These stories underscore the importance of LTAC care in improving patient outcomes, enhancing the quality of life, and fostering resilience and recovery.